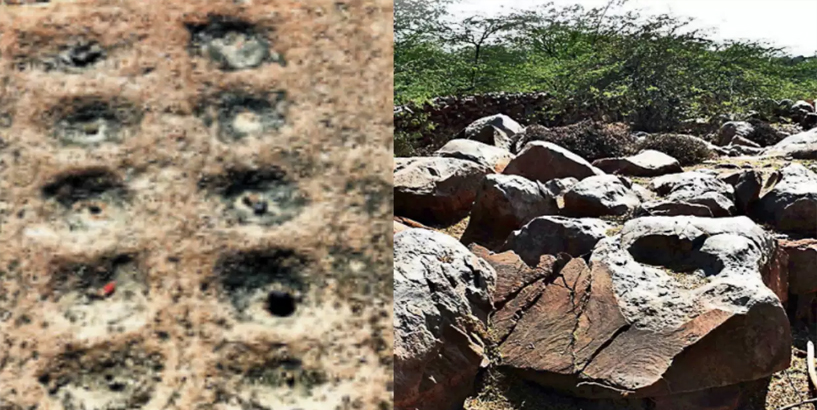
This month, experts will trek up to a 5,000-hectare area in the Aravalis of Mangar and Kot in Faridabad to figure out how far back the stone-age carvings go. A team of the Archeological Survey of India (ASI) will rely on carbon dating to assess the exact age of the carvings. In 2021, ecologist and wildlife researcher Sunil Harsana discovered cave paintings and stone carvings across Shilakhari, Mangar, Kot, Dhauj, Roj ka Gujjar, Dhauj and Nurpur Dhumaspur. At the time, archaeologists said this may be the largest stone carving site of the paleolithic era in the Indian subcontinent. Apart from this, pebble and stone tools found at the site — not too far from the Mangar Bani sacred grove — also indicated that human settlers used to manufacture them there. Haryana government officials said on Sunday that the experts will carry out large-scale excavations, radiocarbon dating and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) of the carvings as well as sediments for analysis. After this survey, the process can begin to conserve the area as an archaeological site, said Haryana principal secretary (archaeology and museums) MD Sinha.“As we do not have the expertise to determine the exact period this site belongs to, we need agencies to do carbon dating. We will eventually proceed to protect the site once we are sure that they are associated with palaeolithic age,” Sinha told
The paleolithic era is a period between 2.5 million years ago to 10,000 years before present (BP), when humans lived in caves or rudimentary huts, and used basic stone and bone tools for hunting. Carbon dating involves a study of markers that give away the age of an organic item. AMS is the process used to separate carbon isotopes for dating. Banani Bhattacharyya, deputy director of the directorate of archaeology and museums in Haryana, said the ASI team will be visiting the site soon. “ASI has formed a five-member team. I am also part of the team along with four other experts. We will submit the report after evaluation,” she said. To protect the site, the archaeology and museums department had sent a proposal to the state government, to notify the 5,000-hectare area under Section 4(1) of the Punjab Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1964. The Aravalis of south Haryana have emerged as a treasure trove of archeological findings in recent years. In 1986, stone carvings were discovered at 43 sites in Faridabad’s Anangpur, pivoting archaeologists’ attention to the area. Just this year, Harsana also discovered stone-age hand- and foot-prints, graffiti and shapes of animals engraved on quartzite rocks in a 2km radius area of Badhshapur Tethar village in Sohna. “These findings suggest the Aravalis were occupied by early settlers. Humans have been knapping here, and this is a good indicator of settlements,” Bhattacharyya said.
A team of the Archeological Survey of India (ASI) will rely on carbon dating to assess the exact age of the carvings.
The paleolithic era is a period between 2.5 million years ago to 10,000 years before present (BP), when humans lived in caves or rudimentary huts, and used basic stone and bone tools for hunting.
Field group
fieldgroup is an Indian company established in 2011 that provides solutions on Printing, Book Printing, Offset Printing, information technology, software solutions, web design, Application development, consultancy, e-commerce solutions, publication, and business process services. It is headquartered in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.